Chapter 11
Photoelectric Effect
The phenomenon of emission of electrons from the surface of a metal due to the effect of light is called photoelectric effect.
The electrons emitted in this way are called light electrons or photo electrons. If the circuit is closed, then the flowing current is called photoelectric current.
Hertz and Lenard's experiments
Scientists Hertz, Leonard and Milken conducted many experiments on photoelectric emission. They took plates of different types of metals and made light of different intensities and different frequencies fall on them and measured the maximum kinetic energy and photoelectric current of the emitted electrons in each condition. Thus, they obtained many relations of the photoelectric effect.
Effect of light intensity –
When light is incident on the surface of a metal, if the frequency of light is appropriate, light electrons start emitting from the surface. When the intensity of the incident light is increased, the value of photoelectric current also increases in almost the same proportion.
Effect of frequency of light –
When a graph is drawn by taking the frequency of the incident light on the x-axis and the maximum kinetic energy of the light electrons on the y-axis, a straight line is obtained. This means that when the frequency of the incident light is high, the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted light electrons is also high.
Ek = A(υ - υ o )
Threshold frequency
The minimum frequency of incident light that can emit light electrons from the surface of a metal is called the threshold frequency. It is represented by u o .
- If u > u o then light electrons will be emitted.
- If u < u o then light electrons will not be emitted.
- The value of threshold frequency is fixed for a given material and its value is different for different materials.
Threshold Wavelength
The maximum wavelength of incident light that can cause emission of light electrons from the surface of a metal is called the threshold wavelength. It is expressed as λo.
- [λ o = c/υ o ] where c – speed of light
- If λ < λ o then light electrons will be emitted.
- If λ>λ o light e will not be emitted.
qualitative nature theory of light
According to Planck's quantum theory, light travels in the form of small bundles or packets of energy. This bundle of energy is called a photon or quantum.
The energy of each photon is E=hυ, where υ is the frequency of light and h is Planck's universal constant. Its value is 6.62X10 -34 joule-second. The intensity of light depends on the number of these photons. If the wavelength of light is λ and the speed of light in vacuum is c, then the energy of the photon = hc/λ
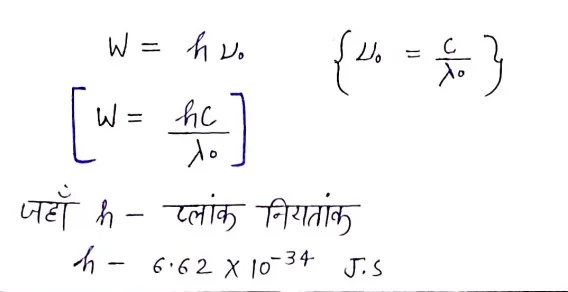
Work function
The minimum energy that can emit light electrons from the surface of a metal is called the work function. It is expressed as w.
Mathematician – is electron volt (ev) or J (joule).
Stopping Potential
The minimum negative potential given to the plate (anode) relative to the cathode, at which the value of photoelectric current becomes zero, is called the stopping potential or stopping potential. It is expressed as V o .
Experimental laws of photoelectric effect
On the basis of experiments the following rules were formulated –
- The value of photoelectric current depends on the intensity of the incident light.
- The maximum kinetic energy of photo electrons does not depend on the intensity of the incident light.
- The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted light electrons depends on the frequency of the incident light.
- If the frequency of the incident light is less than the threshold frequency for the metal, then no matter how intense the light is, or how long it is incident, emission of light electrons cannot occur.
- As soon as light falls on the metal surface, light electrons start getting emitted from the surface, that is, there is no time lag between the incidence of light and the emission of light electrons.
Einstein's photoelectric equation
Einstein explained on the basis of German scientist Max Planck's quantum theory that when a light photon falls on a metal surface, the energy (hv) of the photon is divided into two parts. The first part brings the light electron to the metal surface, which is called work function (w). The second part of the energy provides maximum energy (E k ) to the light electrons.
hυ=W+ Ek
Einstein's photoelectric equation is:- ½ mv² max =h (υ-υ o )
Matter Waves
When a particle (photon) moves, a wave is always associated with that particle, this wave is called matter wave.
The wavelength of waves related to different particles is different.
Expression for de Broglie wavelength
λ=h/p
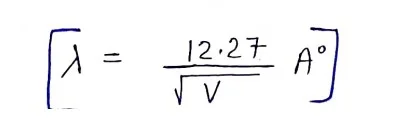
de Broglie wavelength associated with the electron

Comments
Post a Comment